In a study published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer December 2019 issue1, researchers demonstrate that a baseline serum biomarker signature that correlates with Nivolumab drug clearance is also prognostic for overall survival in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Earlier studies indicated that a composite signature was also prognostic for overall survival in melanoma and non-small cell lung cancers2.
Baseline cytokine levels in serum samples were measured from patients with RCC using a CustomMAP immunoassay panel and testing panel performed in Myriad RBM’s CLIA certified lab.
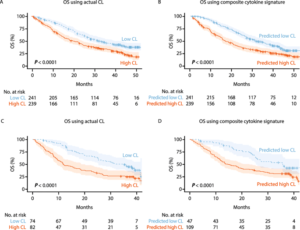
Using data from a training set, researchers used a machine-learning algorithm to identify a baseline composite cytokine signature composed of eight biomarkers that were correlated with Nivolumab drug clearance. The biomarkers were C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin (FRTN), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), alpha 2-macroglobulin (A2Macro), stem cell factor (SCF), vascular endothelial growth factor-3 (VEGF-3), and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). This signature was then applied to an independent validation data set and the correlation to Nivolumab clearance confirmed, with an accurate prediction of low or high Nivolumab clearance. Based on earlier data linking Nivolumab clearance with overall response, the researchers then tested whether the biomarker prediction of low or high Nivolumab clearance was correlated with overall survival.
Fig 1. The correlation of Nivolumab clearance prediction to overall survival. Statistical differences were seen between the groups in both training (A and B) and test (C and D) data sets, with low clearance and predicted low clearance both associated with longer overall survival1.
The combination of results highlights the value of a multi-biomarker signature for RCC prognosis. Many of the markers have already been shown to have association with RCC or other types of cancer patient outcomes. Using multiple markers may show an improved predictive outcome than individual markers alone.
In addition, this finding has the potential to help with balancing patients during clinical trial enrollment between experimental vs comparator arms with respect to drug clearance rate composite cytokine signatures could predict high clearance that significantly associates with high risk, poor prognosis, and shorter overall survival. Such data has already been reported in a similar study in melanoma patients to support the benefits of using a composite biomarker signature in predicting drug clearance2.
References:
- Wang, R., Zheng, J., Shao, X. et al. Development of a prognostic composite cytokine signature based on the correlation with nivolumab clearance: translational PK/PD analysis in patients with renal cell carcinoma. j. immunotherapy cancer 7, 348 (2019) doi:10.1186/s40425-019-0819-2
- Wang, R., Shao, X., Zhen, J., et al. A Machine-Learning Approach to Identify a Prognostic Cytokine Signature That Is Associated With Nivolumab Clearance in Patients With Advanced Melanoma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2019) doi: 10.1002/cpt.1724. [Epub ahead of print]