The Immunomodulatory Effects of Cancer Therapy on IFN-gamma Responses in the Periphery.
(2017) Brunet LR, et al. SITC 2017 Annual Meeting; November 8-12, 2017; National Harbor, MD, USA. Poster 81.
The interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) pathway is an important pharmacodynamic biomarker for immuno-oncology therapies. IFN-γ signatures from tumor tissue have prognostic and predictive potential, yet the potential of IFN-gamma as a biomarker for immuno-oncology is hampered by the difficulty in routinely obtaining tissue from solid tumors and the extremely low levels of circulating IFN-γ in blood.
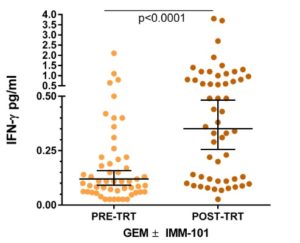
Myriad RBM’s Ultrasensitive Interferon-γ Simoa immunoassay that can accurately quantify IFN-γ in healthy subjects was used for analysis of serum samples from a Phase 2 study of advanced pancreatic cancer. Patients were treated with Gemcitabine +/- IMM-101 (heat killed Mycobacterium obuense) and a significant increase in serum levels of IFN-gamma was observed post-treatment in the IMM-101 treated patients that may be indicative of an improved response to IMM-101 immunotherapy.
Individual levels of IFN-g protein measured by IFN-g Simoa™ immunoassay in serum samples of advanced pancreatic cancer patients recruited to IMAGE-1, prior to the start of treatment (n=53) and post-treatment (n=54). The bars indicate geometric mean ± 95% CI. Statistical analysis was performed by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. (Brunet et al.)
The ability of IMM-101 to enhance IFN-gamma responses in vivo was confirmed in two pre-clinical mouse models.
For more information:
- The Immunomodulatory Effects of Cancer Therapy on IFN-gamma Responses in the Periphery –
View the poster - Development & Validation of Ultrasensitive Simoa-based Immunoassay Services – On Demand Webinar
- Immuno-oncology Biomarkers: pharmacodynamic and prognostic blood-based proteins – Read how MAP testing analysis has been used to advance clinical trials